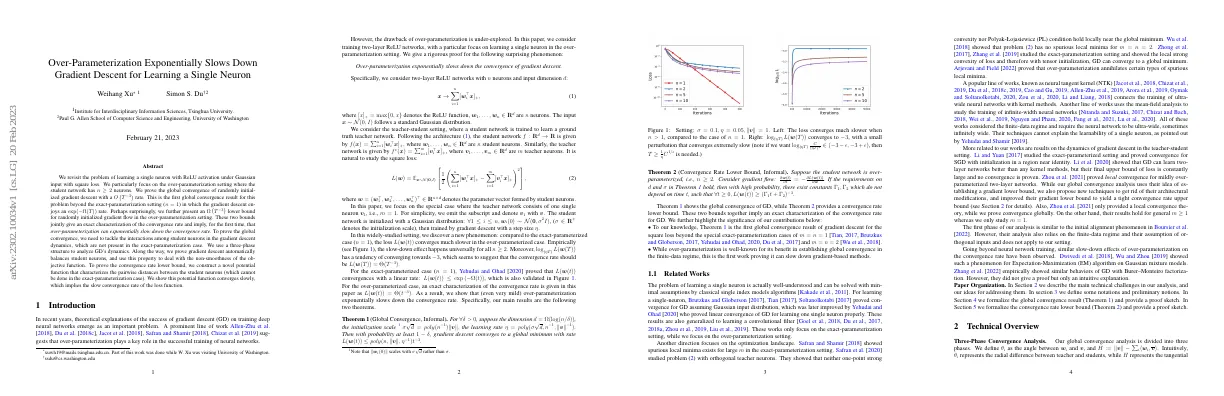
Regularised neural networks mimic human insight
Link to paper The full paper is available here. You can also find the paper on PapersWithCode here. Abstract Humans can show sudden improvements in task performance linked to insight Artificial neural networks can also show insight-like behaviour Insight-like behaviour in neural networks is caused by noise, attentional gating and regularisation Paper Content Introduction Ability to learn from experience is common to animals and some artificial agents Neural networks trained with SGD are a current theory of human learning Humans may sometimes learn in an abrupt manner Insights occur when an agent finds a novel problem solution by restructuring an existing task representation Insights involve unconscious processes becoming conscious Insights can be accompanied by a feeling of relief or pleasure Insights are related to brain regions distinct from those associated with gradual learning Insight-like behaviour can emerge from gradual learning algorithms Insights trigger abrupt behavioural changes Insights occur selectively in some subjects Insights occur “spontaneously” without external cues Regularisation and gating can cause discontinuities in learning in neural networks Results 99 participants and 99 neural networks performed a decision task Task required a binary choice about circular arrays of moving dots Dots were characterized by two features with different degrees of noise Task provided a hidden opportunity to improve one’s decision strategy Initial training phase only motion direction predicted correct choice Later phase both features could be used to determine choice Post-experimental questionnaire asked if participants noticed a rule, how long it took, and if they paid attention to colour Human behaviour Participants learned the response mapping for the four motion directions well Noise was added to the motion, while the colour remained uncorrelated Performance was heavily diminished in the conditions with the largest amounts of motion noise Performance improvements largely beyond these low baseline levels can only be attributed to colour use Noise level continued to influence performance in the motion and colour phase Onset of the colour correlation triggered performance improvements across all coherence levels 57....