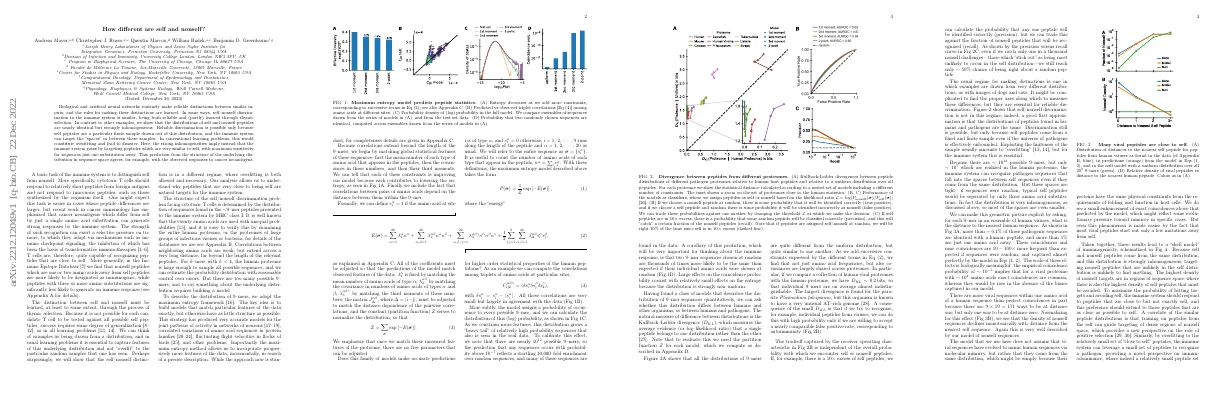
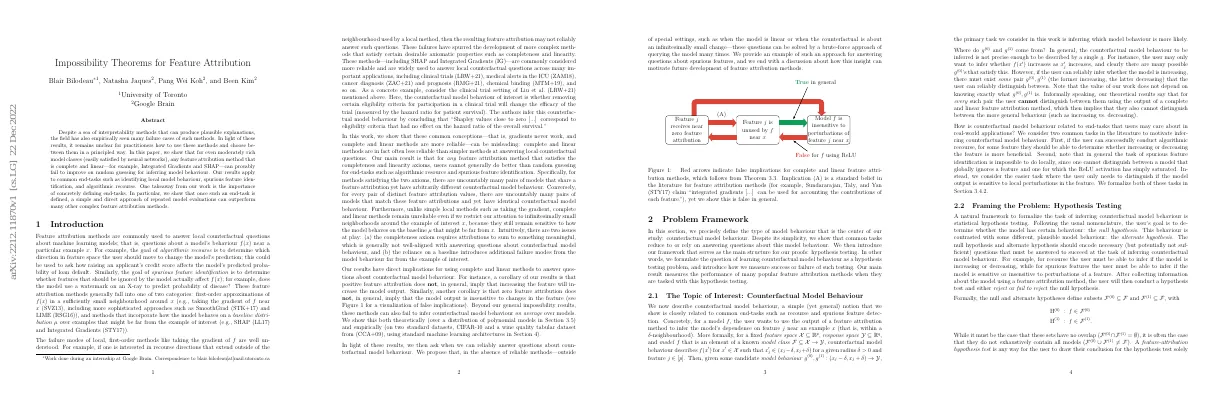
Link to paper The full paper is available here.
You can also find the paper on PapersWithCode here.
Abstract Capturing and merging frames to enhance an image disregards 3D nature of scene 42 12-megapixel RAW frames captured in 2-second sequence can recover high-quality scene depth Test-time optimization approach fits neural RGB-D representation to long-burst data Plane plus depth model is trained end-to-end and performs coarse-to-fine refinement Geometrically accurate depth reconstructions with no additional hardware or separate steps Paper Content Introduction Rise and fall of film and DSLR photography Cellphones offer high megapixel image streams On-board motion measurement devices Integrated active depth sensors Depth imaging and 3D reconstruction Depth can help with object understanding Depth can help compensate for non-ideal camera hardware Depth can be used for augmented reality and interactive experiences Many ways to produce depth Apple iPhone 12-14 Pro devices use depth derived from RGB Existing passive monocular depth estimation methods Multiview depth estimation methods Neural radiance field approaches Millimeter-scale view variation from natural hand tremor Unsupervised end-to-end approach to estimate depth and camera motion Jointly distill relative depth and pose estimates Evaluations demonstrate approach outperforms existing methods Related work Depth estimation can be divided into active and passive methods Active methods use controlled illumination to infer object shape or improve stereo feature matching Time-of-flight (ToF) depth sensors use round trip time of photons to infer depth Passive methods use correlation between visual and geometric features to estimate 3D structure Multiview and structure from motion works leverage epipolar geometry to extract 3D information from multiple images Neural scene representation works learn an implicit representation of a 3D scene by fitting a multi-layer perceptron to a set of input images Our work uses a neural representation of RGB to distill high quality continuous representations of both depth and camera poses Long-burst photography Burst photography is a type of imaging where multiple frames are taken in rapid succession Parameters such as ISO and exposure time can be varied during capture Burst imaging pipelines investigate how these frames can be merged into a single higher-fidelity image Video processing literature operates on sequences hundreds of frames in length and/or large camera motion Long-burst photography is several seconds of continuous capture with small view variation Data collection tool was designed to record two-second, 42 frame long-bursts RAW images are preserved with 14-bit color depth and minimal processing Unsupervised depth estimation Proposed a method for depth estimation from long-burst data Assessment Comparing approach to BARF, SfSM, iPhone 14 Pro, MiDaS, RCVD, and HNDR All baselines run on processed RGB data except HNDR Assessing absolute performance and geometric consistency with 3D objects scanned by a commercial high-precision turntable structured light scanner Outperforming existing learned, mixed, and multi-view only methods Reconstructing small features such as Dragon’s tail, Harold’s scarf, and the ear of the Tiger statue Plane plus depth offset approach avoids spurious depth solutions in low-parallax regions Producing high-quality object reconstructions Quantitative depth metrics outperform all comparison methods RAW long-burst data can improve depth reconstruction compared to 8-bit RGB Discussion and future work It is possible to recover high-quality, geometrically-accurate object depth from a stack of images acquired during long-burst photography....