Link to paper The full paper is available here.
You can also find the paper on PapersWithCode here.
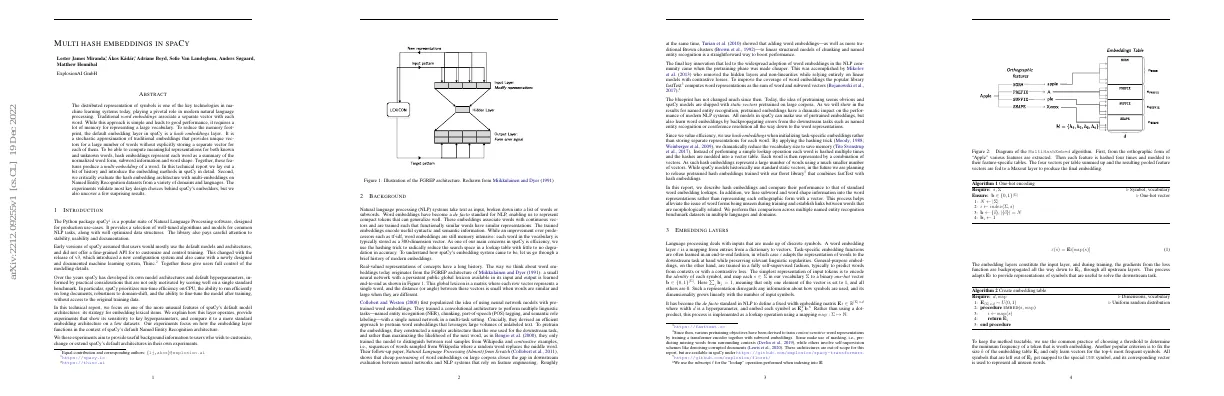
Abstract Distributed representation of symbols is important in machine learning systems Traditional word embeddings associate a separate vector with each word Hash embeddings reduce memory footprint by representing each word as a summary of normalized word form, subword information and word shape Technical report introduces embedding methods in spaCy and evaluates hash embedding architecture with multi-embeddings on Named Entity Recognition datasets Paper Content Introduction SpaCy is a popular suite of Natural Language Processing software It provides algorithms and models for common NLP tasks It pays attention to stability, usability and documentation It offers a fine-grained API for customizing and controlling training It prioritizes run-time efficiency, long document efficiency, robustness to domain-shift, and the ability to fine-tune the model It uses the hashing trick to reduce the search space in a lookup table Word embeddings associate words with continuous vectors They encode useful syntactic and semantic information Collobert and Weston popularized the idea of using neural networks with pretrained word embeddings Mikolov et al....